See informational videos on TreeLafayette.TV channel on YouTube, including videos on trees, how to plant trees, how to care for trees, information about trees, etc.
For information about trees, use one of the links below. See two myths about trees at the bottom of the page.
General Information About Trees:
- The Benefits of Trees
- Types of Trees
- Self-Guided Tree Tours on Purdue University Campus
- USDA Plant Database
- Tree and shrubs that are good for bees
- Tree Owner’s Manual
How to Choose or Identify Trees:
- How to Choose a Tree
- City of Lafayette Tree Species Recommendations
- Indiana DNR Tree Sales Database (saplings)
- Arbor Day Foundation Tree Database
- Indiana Native Plant and Tree Information
- Field Guide to Trees
- Arbor Day Foundation Best Tree Selection Wizard
- My Tree Benefits from i-Tree (Tell a little bit about your tree and it will estimate the amount of carbon dioxide and pollution it removes from the air, as well as the amount of stormwater it can help mitigate.)
- Alternatives to ash trees
- Native trees of Indiana
How to Plant a Tree:
- Plant the right tree in the right place
- How to Plant a Tree
- Tree Planting Detail
- Tree Staking Detail
How to Care for Trees:
- The Reasons to Prune a Tree
- How to Prune a Tree
- Pruning a Tree
- Tree Pruning Essentials
- Watering trees (newly planted trees need about 10 gallons of water per week after planting) (newly planted saplings need less water each week and for a shorter period of time)
Tree Issues:
- Purdue University Plant Doctor – Get helpful infomation about plant issues.
- Purdue University Plant Doctor quick video guides – Guides on YouTube
Tree Myths:
Myth #1: Tree roots cause sidewalk damage.
Typically, sidewalk damage is the result of poor soil conditions and improper construction. If gaps are created due to pavement heaving and settling with the soil, roots will naturally follow these spaces. And if sidewalks are poured too thin, they are more prone to lifting and cracking from tree roots. Sidewalks need to be installed properly, especially if soil conditions are poor. Once the tree roots are drawn to the poorly installed sidewalk, they can lift the sidewalk as the tree roots grow. Any tree close to a sidewalk also needs to be installed properly, especially at the proper depth. The tree roots may stay near the ground level if the tree is not planted properly.
Myth #2: Tree roots break sewer lines.
In favorable soil conditions, including moisture, texture, and oxygen, most roots are found in the top 24″ of soil – well away from sewer pipes. A few tree species, however, may grow deeply enough to be near a properly buried sewer line so plant the right tree at the right place. Even so, nothing happens until the sewer pipe breaks or leaks. Nearby roots then begin to thrive and grow rapidly. They can enter the defective pipe and eventually block the flow of sewage. Failing sewer pipes draw tree roots to them with the moisture and nutrients.
Trees and Utilities (Overhead and Underground)
The Right Tree in the Right Place should be kept in mind when planting trees.
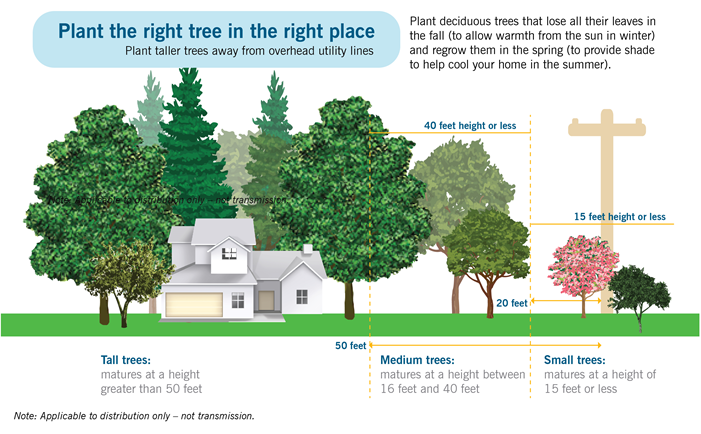
If you have questions about rules to planting around overhead or underground utilities, contact the relevant utility company.

